Hard Evidence of Early Human Seafaring and Women’s Role in Marine Foraging
New and fascinating discoveries provide hard evidence for the Aquatic Ape theory, evidence that was not known when Alister Hardy and Elaine Morgan first advocated for this idea. There is now substantial data proving that early humans undertook long maritime journeys, developed unique physiological adaptations, and lived lives closely tied to water. In this blog post, I will examine some of the compelling evidence that supports a semi-aquatic past for humans. These pieces of evidence meet the stringent criteria set by the anthropological community, which demands archaeological proofs for our evolutionary history, rather than merely examining our own bodily adaptations.
Long Early Maritime Journeys
Early human species undertook impressive sea voyages, as evidenced by discoveries of human fossils and stone tools on distant islands that have been separated from the mainland for millions of years. For instance, Homo sapiens reached Australia about 65,000 years ago, a journey that required crossing at least 70-100 km of open sea from Indonesia, traversing the significant biogeographical barrier known as Wallace Line (O’Connell, Allen, & Hawkes, 2010). Similarly, Homo heidelbergensis or Neanderthals reached Crete around 130,000 years ago, leaving hand axes behind and crossing water distances of approximately 40 km (Strasser et al., 2010).
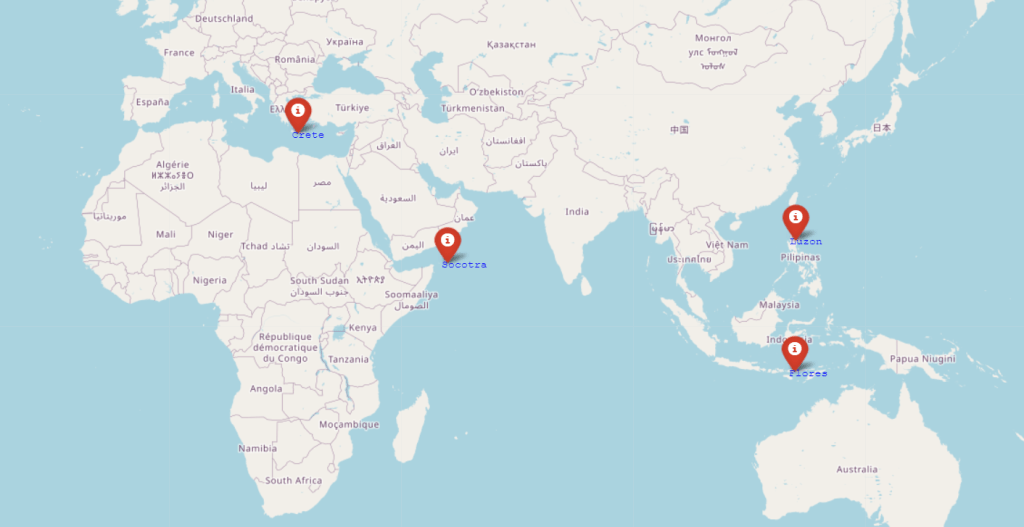
Even more spectacular are the colonization events of Luzon in the Philippines, Socotra in the Indian Ocean, and Flores in Indonesia. The colonization of Luzon, evident from the discovery of Homo luzonensis dating back 67,000 years, required crossing the Huxley Line, another notable biogeographical barrier, involving a journey of at least 250 km from the nearest landmasses (Detroit et al., 2019). Evidence also suggests that Oldowan toolmakers reached Socotra several hundred thousand years ago, which would have required a sea journey of approximately 80 km from the African coast (Amirkhanov et al., 2009). Additionally, the colonization of Flores, marked by the discovery of Homo floresiensis, also known as the Hobbit, required a journey of around 30-40 km of open sea (Morwood, Oosterzee, & Sutikna, 2007).

It is likely that Socotra, Flores, and Luzon were places where more archaic human species could live relatively undisturbed for long periods. For instance, the discovery of Oldowan tools on Socotra, which first appeared around 2.6 million years ago and were made by the ancestors of Homo erectus, suggests a very ancient colonization of the island (Semaw, 2000; Amirkhanov et al., 2009). The first settlers on Flores and Luzon were also likely from species predating Homo erectus, based on analyses of the fossils of Homo floresiensis and Homo luzonensis, which exhibit some archaic features (Morwood, Oosterzee, & Sutikna, 2007; Detroit et al., 2019). Given that these are all very isolated islands, it is entirely possible that early hominids lived throughout much of Southeast Asia for extended periods but were eventually pushed out when Homo erectus settled in the region, surviving late only on islands far out at sea.
All this evidence indicates that humans have been well-acquainted with aquatic environments for a couple of million years and suggests that humans probably lived scattered throughout the maritime world of the Eurasian coastline. This is also a clear sign that they could build floating structures or boats to undertake these maritime journeys.
Clues from Kalambo Falls
One clue to how these early floating structures might have been constructed can be found at Kalambo Falls in Zambia. Archaeologists have discovered the oldest known wooden structures here, dated to around 476,000 years ago. These structures consist of two interlocking logs joined by an intentionally cut notch. The researchers behind this finding believe the structures were likely used as a stable platform in a wet environment, which may have included use as a raft or dock (Barham et al., 2023).
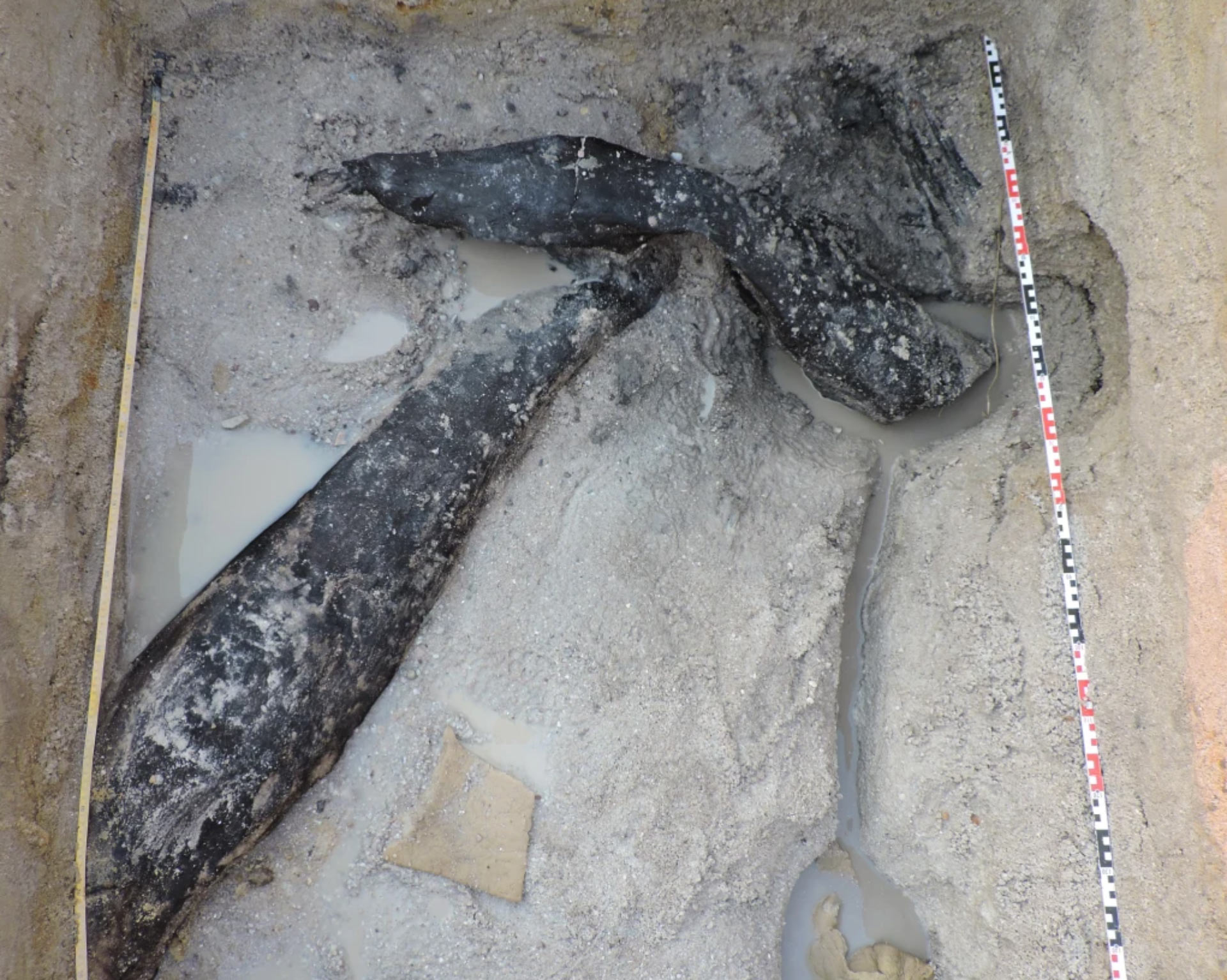


The preservation of these wooden structures was possible because they became waterlogged, meaning they were submerged in water and saturated, preventing decomposition by creating an anaerobic (oxygen-free) environment (Barham et al., 2023). This remarkable preservation provides further evidence of early humans’ ability to use wood to create structures for aquatic activities.
Surfer’s Ear: Evidence of Aquatic Adaptations in Early Humans
Surfer’s ear, or exostosis, is a bony growth in the ear canal that develops from prolonged exposure to cold water. Research by Trinkaus, Samsel, and Villotte (2019) has shown that a significant percentage of both Neanderthal and early Homo sapiens fossils in Eurasia exhibit this condition. In a study examining 77 fossils with well-preserved ear canals, it was found that these early humans were frequently in cold water environments, likely for marine foraging activities (Trinkaus, Samsel, & Villotte, 2019).
In the study, 48% of the Neanderthal specimens investigated had Surfer’s ear. While it was often difficult to determine their sex, among the identified Neanderthal women, three out of four had this condition (Trinkaus, Samsel, & Villotte, 2019). Similarly, Surfer’s ear was prevalent in Homo sapiens fossils, with approximately 25% of Middle Paleolithic specimens (300,000 to 30,000 years ago) showing the condition. The prevalence was 20.8% during the Early/Mid Upper Paleolithic (50,000 to 30,000 years ago) and dropped to 9.5% in the Late Upper Paleolithic (30,000 to 10,000 years ago), indicating a change in lifestyle (Trinkaus, Samsel, & Villotte, 2019).
Interestingly, in the 19 sexable Early/Mid Upper Paleolithic Homo sapiens specimens, Surfer’s ear was present in 16.7% of males and 28.6% of females. This suggests that more women than men exhibited this condition in early Homo sapiens (Trinkaus, Samsel, & Villotte, 2019). These findings support the hypothesis that women, due to their thicker layer of subcutaneous fat, were better suited to spending extended periods in water and were likely more involved in diving activities. This evidence highlights the significant role aquatic environments played in the lives of early humans.
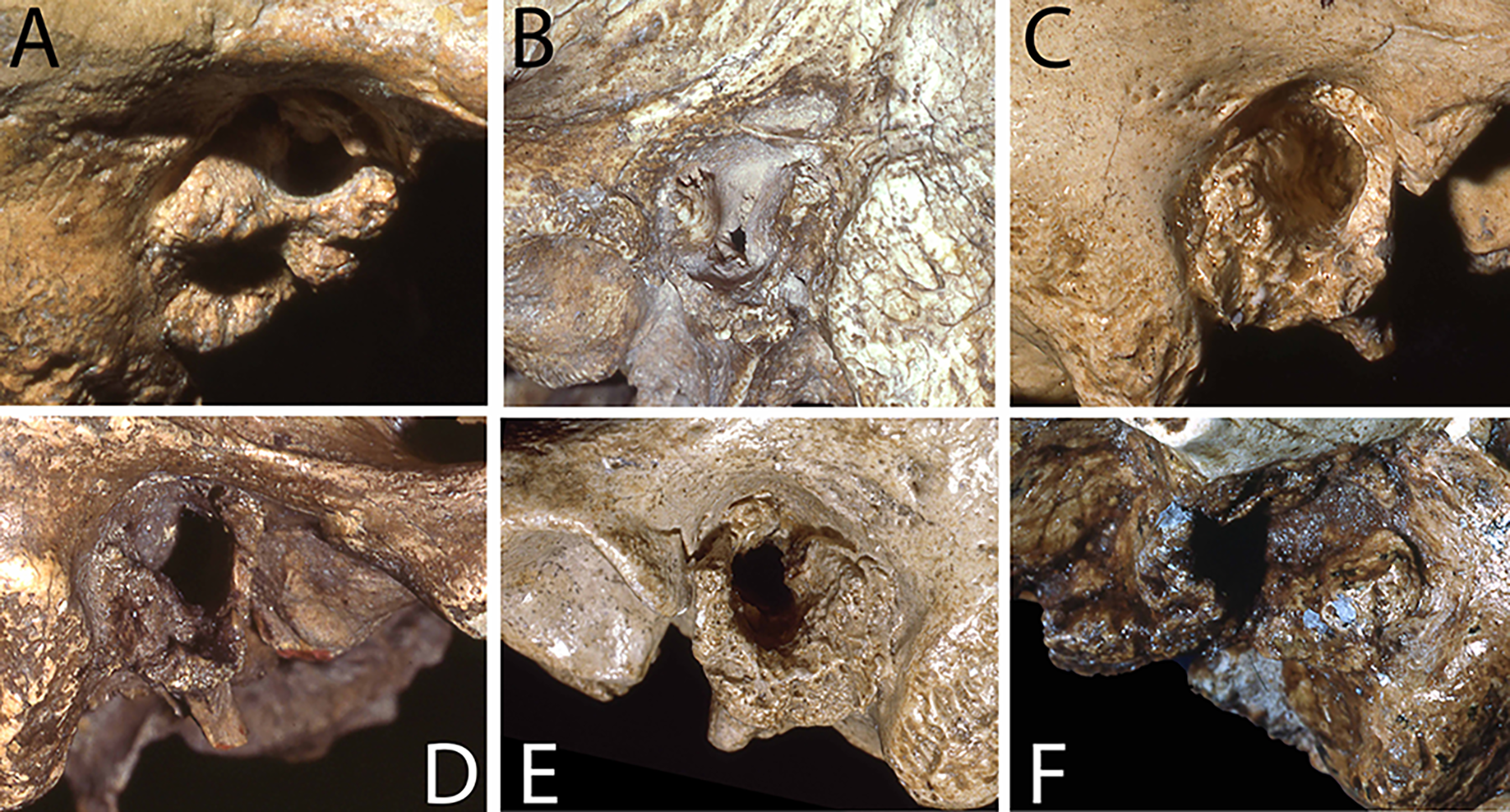
Moreover, findings from Panama show that even people living in warm environments can develop Surfer’s ear when they engage in deep diving where the water is colder. This observation is supported by the analysis of fossils dating back thousands of years (Arias-Martínez et al., 2019), further emphasizing the connection between human activity and aquatic environments across different climates and time periods.
Conclusion
These pieces of evidence collectively paint a compelling picture of how early humans thrived in and around water. From navigating long distances over open seas to developing physiological adaptations to cold water environments, much also indicates that women were perhaps more involved than men in diving activities during this time.
As we uncover more about our past, it becomes clear that our relationship with water has profoundly shaped our evolution. These findings not only challenge previous notions about early human behavior but also open new avenues for understanding the complexities of our development. The future of exploring our aquatic heritage lies in continued research and the growing field of underwater archaeology, promising even more fascinating discoveries.
Literature
Amirkhanov, K. A., Zhukov, V. A., Naumkin, V. V., & Sedov, A. V. (2009). Эпоха олдована открыта на острове Сокотра. Pripoda, 7.
Arias-Martínez, L., González-Reimers, E., Velasco-Vázquez, J., Santolaria-Fernández, F., & Hernández-Moreno, M. (2019). Auditory exostoses and their relationship to environmental factors in the pre-Hispanic Canary Islands. American Journal of Physical Anthropology. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ajpa.23757.
Barham, L., et al. (2023). Earliest Evidence of Structural Use of Wood at Kalambo Falls. Nature. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06557-9.
Detroit, F., Mijares, A. S., Piper, P., Grün, R., Bellwood, P., Aubert, M., … & Zeitoun, V. (2019). A new species of Homo from the Late Pleistocene of the Philippines. Nature, 568(7751), 181-186.
Morwood, M. J., Oosterzee, P. V., & Sutikna, T. (2007). The Discovery of the Hobbit: The Scientific Breakthrough that Changed the Face of Human History. Random House.
O’Connell, J. F., Allen, J., & Hawkes, K. (2010). Pleistocene Sahul and the Origins of Seafaring. Cambridge Archaeological Journal, 20(1), 69-84. doi:10.1017/S0959774310000055.
Strasser, T. F., Panagopoulou, E., Runnels, C. N., Murray, P. M., Thompson, N., Karkanas, P., … & Coleman, J. (2010). Stone Age seafaring in the Mediterranean: evidence from the Plakias region for Lower Palaeolithic and Mesolithic habitation of Crete. Hesperia: The Journal of the American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 79(2), 145-190.
Trinkaus, E., Samsel, M., & Villotte, S. (2019). External auditory exostoses (Surfer’s ear) in the human fossil record: A proxy for behavioral adaptations to aquatic resources. PLOS ONE, 14(8): e0220464. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0220464.
The Rise of Modern Behavior: A Copernican Revolution in Understanding Human Evolution
Have we misunderstood the true essence of human evolution and the role of language in our ancient past? In a new article, I propose a Copernican shift in our understanding of language’s original function and the cognitive revolution that began approximately 75,000 years ago.
Traditional views hold that language evolved primarily as a tool for enhanced communication and complex thought. However, this article suggests that language’s original role was more about replicating behaviors linked with tool use, transferring these behaviors from one generation to the next through singing and rhythm. Initially, language served to reconcile the gap between the human body and its environment, which arose with the advent of the first stone tools, enabling early humans to navigate landscapes for which they were not biologically adapted.
This theory resolves a longstanding paradox since the inception of evolutionary theory: although thinking has an evolutionary past, and Homo sapiens are estimated to be 300,000 years old, humans have not always been ‘modern.’ What if humans are not inherently meant to think and act as they do today? What if evolution promoted aspects other than intellectual capability? Accepting this paradox might mean acknowledging that humans have undergone both a gradual evolutionary process, as Darwin suggested, and a rapid developmental leap, as indicated by archaeological findings—without any genetic change in the brain.
This new theory draws support from a diverse array of disciplines. Archaeological records reveal sporadic bursts of creativity alongside a gradual brain development; meanwhile, studies on mirror neurons offer a neurological basis for mimicry and observational learning, essential for transmitting skills and behaviors across generations. Additionally, theories about our aquatic past propose that water-based environments laid the groundwork for the evolution of vocalization and singing. Insights into how children acquire language—focusing on the roles of intonation and rhythm—mirror the significant role that song played over speech. These interdisciplinary findings suggest that our evolutionary path was not a straightforward march towards greater intellectual capability but rather a complex journey marked by periods of significant conformity punctuated by bursts of creative potential since the first stone tools 2.6 million years ago. This perspective helps explain not only the creative outbursts in South Africa 75,000 years ago but also other instances of early possible symbolic behavior, such as the use of shell beads by early Homo sapiens and Neanderthals.
Moreover, this perspective aligns with various global mythologies that narrate an ancient, harmonious coexistence with nature, disrupted by the cognitive revolution. Could the hauntingly beautiful cave paintings, some of the earliest known forms of human art, be interpreted not just as artistic expressions but as calls for help? These artworks could be seen as profound expressions of a deep-seated longing for reconnection with the natural world we once knew.
You can find the article here: The Rise of Modern Behavior: A Copernican Revolution in Understanding Human Evolution
Life of Sama Dilaut – Broken Eardrums, Spear Gun Fishing and Indebtedness
From the end of December 2016 to the beginning of February 2017 I travelled in Philippines, Malaysia and Indonesia where I visited several Sama Dilaut communities. I talked to them about their daily lives, followed fishing and continued to learn the basics of two of their dialects, Central Sinama and Indonesian Bajo.
Noah – one of the last young boys who make a living from spearfishing in Davao
The trip started in Matina Aplaya in the outskirts of the metropolis Davao City in southern Philippines. Fish is on the decline and most people in the village make a living from vending of pearls, second hand clothes and shoes. However, a few families still make a living from the sea, and they are incredible divers.
I have been visiting Matina Aplaya every year since 2010 and I have always been accompanied by Issau and his son Noah. Noah is one of the few boys in the village who has grown up becoming a skin diver along with his father. On daily fishing expeditions, they spear fish and collect sea urchins, sea shells and clams in the coral reefs surrounding the town. It is fascinating to see that Noah has grown up to become a skilled fisherman who contributes to the household with his spear gun.
Zamboanga – Sama Dilaut resettlement after the 2013 fire
In 2013, the outskirts of Zamboanga were struck by a fire that destroyed thousands of houses and displaced thousands of Sama Dilaut and Tausug people. For months, they were living in a temporary camp in a sport arena close to the town centre.
After my visit in Davao, I made a two-day stopover in Zamboanga in western Mindanao before travelling to Tawi-Tawi. I visited some newly constructed villages set up by NGO:s and local authorities exclusively for the Sama, and many of the houses have been built in a traditional way. However, the daily life of many Sama Dilaut in Zamboanga is tough and it is getting harder and harder to make a living from the ocean. Many people are begging in the harbour. Yet others have fled to other cities in the Philippines.
Sitangkai – traditional dance in the Venice of the south
Despite recent kidnapping incidents in the Sulu I decided to travel to Tawi-Tawi in southwestern Philippines. I visited the Sama Study Center and the Marine museum in Tawi-Tawi where I met Rasul M. Sabal, the museum director. He has a keen interest in Sama Dilaut culture and show sincere concern with their challenges.
While in Tawi-Tawi I took the opportunity to pay a visit to Sitangkai along with Rasul M. Sabal and two policemen. Over the last years, very few foreigners have been in the area and I was fortunate to be able to visit the legendary community where thousands of people live in what is called the “Venice of the south” next to a tiny piece of land.
In Sitangkai, Sama elders performed religious dance that is normally performed during the magpai baha’u ceremony, an annual ritual taking place once a year in community (this year it will be held in May and it attracts Sama people from all over Sulu and Sabah). It was great to experience their hospitality and kindness!
I came to know that the interaction between Sabah and southern Philippines is intense despite stricter migration policies on the Malaysian side, and boats are heading between the locations more or less every night. In Sitangkai, I also saw how octopuses were shipped on a large scale to Tawi-Tawi and further to Zamboanga and Manila. However, the production of sea weeds has dropped due to reduced market prices.
Broken eardrums
After Tawi-Tawi, the initial plan was to take a ferry to Semporna, but the ferry company had lost its license so I took another ferry going back to Zamboanga instead. In the harbour of Bongao, more than 20 Sama Dilaut children were diving for coins, displaying great skills.
On the trip back to Zamboanga, I met two Sama brothers from Tawi-Tawi who were on their way to Palawan to join a fishing crew going deep in the South China Sea. They told me that they usually made use of explosives and compressors during these trips, and that the expeditions used to last for about one month. I asked them about their eardrums, and they said that they had broken them. Then, I asked them about their hearing ability, and they told me that their hearing was okay but that they had problems localising sounds. The brothers’ story is interesting since it has been unclear whether Sama fishermen break their eardrums or not. I would say that most the Sama Dilaut divers permanently rupture their eardrums, either on purpose or accidentally, and they take medicine in the case of infection. However, some fishermen do also equalize their ears and some may have hands free techniques for doing so.
When the ferry arrived in Zamboanga day after, the scene changed. Nearly 100 Sama begged for money in the harbour, including elders, and the atmosphere was more tense than in Bongao. It got obvious that life is very difficult in Zamboanga, and it is not surprising that so many Sama Dilaut are now roaming the cities of Manila, Cebu and other Philippine cities.
Meeting with Sulbin on Mabul
After the trip to Sulu, I made a short stop in Semporna where I went to Mabul to meet the Sama community there. I was lucky to meet Sulbin – the diver who walks on the sea floor for nearly two minutes in a widespread BBC production. He told m e that he had just come back from seasonal work in Kota Kinabalu. Hence, also the most skilled fishermen might choose to make a living in the job market rather than make their own fishing trips in the region!
e that he had just come back from seasonal work in Kota Kinabalu. Hence, also the most skilled fishermen might choose to make a living in the job market rather than make their own fishing trips in the region!
However, in Semporna many Sama Dilaut still live in houseboats and they roam the many islands in search of fish, sea shells, clams, sea urchins and so on. Many of the more traditional Sama have no option but to continue extracting resources from the ocean.
Sama Dilaut spear-gun fishing women Wakatobi
After the short stop in Malaysia, I went on to Makassar in Indonesia where I met up with Professor Erika Schagatay from Mid-Sweden University, for our third trip together. We headed towards the island of Buton in southern Sulawesi where we spent a few days in the village of Topa (the sama village where Erika Schagatay first came in contact with Sama people in 1988). In the village, we followed fishing, talked to the people and made physiological research on Sama divers. For example, we measured the diver’s lung capacity, spleen size and feet size.
After the stay in Topa, we took a ferry to Wangi-Wangi in the Wakatobi island group. We spent one day in Wangi-Wangi before we visited the village of Samepla further out in the archipelago, where we spent four days. Sampela is located more than one hundred meters from the island of Kaledupa and have got attention in several film projects throughout the years, in for example BBC:s series “Hunters of th e South Seas” and the movie “The Mirror Never Lies”. During our stay in the village, we joined a group of women spearfishing, and it was fascinating to see their acquaintance with the ocean. We also followed fishing with Tadi, a 70-year-old fisherman who is still an incredible fisherman. He was the most successful fisherman during our trips, outperforming much younger spear gun fishermen. We also got the opportunity to measure Tadi’s spleen, and it turned out that his spleen is much bigger than peoples at the same age and with the same body size, and whom do not make a living from diving. The spleen is a very critical organ for experienced divers, since it consists of a high concentration of blood cells that can be released under pressure.
e South Seas” and the movie “The Mirror Never Lies”. During our stay in the village, we joined a group of women spearfishing, and it was fascinating to see their acquaintance with the ocean. We also followed fishing with Tadi, a 70-year-old fisherman who is still an incredible fisherman. He was the most successful fisherman during our trips, outperforming much younger spear gun fishermen. We also got the opportunity to measure Tadi’s spleen, and it turned out that his spleen is much bigger than peoples at the same age and with the same body size, and whom do not make a living from diving. The spleen is a very critical organ for experienced divers, since it consists of a high concentration of blood cells that can be released under pressure.
Also in Sampela, life is getting more and more difficult because of decline in fish. In the community, there is also a problem of indebtedness and large interest rates. Hence, many Sama fishermen are forced to increase fishing efforts despite recent decline in marine resources. Or in other words, they live on resources yet to be extracted.
Sampela is located within the Wakatobi National Park, but nevertheless, too little is done to prevent over-exploitation of the area. Big fishing boats enter the waters even though only small scale fishing methods are allowed. Hence, more must be done to reinforce the park regulations and to protect the area and the people living there.
Kabalutan – a pregnant woman showing great diving skills
My last visit in Indonesia took place in the community of Kabalutan in the Gulf of Tomini, central Sulawesi. Also this community is known from a few TV productions. Here, BBC produced a short documentary about Sama Dilaut with Tanya Streeter in 2007, in which young Sama children dive 12 meters repeatedly displaying great skills. This is also the place where Svea Andersson’s depicts a eight month pregnant woman diving for shell fish in the movie “Sulawesi, the last sea nomads”.
Along with two Sama families, I followed on a pongka fishing trip – a fishing trip at sea lasting for a few days. We stayed two nights at sea, collecting shell fish and spear-gunned fish. Among those who followed were 17 year old Muspang, the youngest boy in BBC:s movie with Tanya Streeter He is already a father and a great diver. However, I was more impressed by his mother, the same woman that was highlighted in Svea Andersson’s movie. Again pregnant, she was diving up to eight meters in search for shell fish and clams, as well as spear gun fishing. She is one of the last free diving Sama women with great diving abilities; one of the few remaining in not only Kabalutan but most likely in most Sama communities throughout Southeast Asia.
trip at sea lasting for a few days. We stayed two nights at sea, collecting shell fish and spear-gunned fish. Among those who followed were 17 year old Muspang, the youngest boy in BBC:s movie with Tanya Streeter He is already a father and a great diver. However, I was more impressed by his mother, the same woman that was highlighted in Svea Andersson’s movie. Again pregnant, she was diving up to eight meters in search for shell fish and clams, as well as spear gun fishing. She is one of the last free diving Sama women with great diving abilities; one of the few remaining in not only Kabalutan but most likely in most Sama communities throughout Southeast Asia.
However, the amount of large commercial fish in on the decline also in Kabalutan, and it will be difficult for Sama people to sustain a living at the sea. Shell fish and octopus are still in quite big numbers since they mostly are being extracted using traditional fishing methods including diving, but other fish are rare. Who knows what life will look like after just 10 years when the consequences of coral bleaching and rising ocean temperatures will be much more severe than today?
“Homo Erectus were Shallow Water Divers”
Between 8th-10th on May researchers from all over the world gathered in London, presenting new research on human evolution, health and migration – with focus on the so called waterside theory. During the conference we could hear about swimming babies, water births, free diving, indigenous diving, underwater vision, surfer’s ear, coastal migration, bipedalism, aquatic mammals and much more.
Outspoken critics to the aquatic ape theory were also present, as for example Donald Johanson and John H. Langdon. Already in the first session, Donald Johanson declared that the so called aquatic ape theory is nonsense – before he had even heard the arguments that were to be presented during the conference.
The Aquatic Ape Theory has changed since it was first publicized by Alister Hardy and Elaine Morgan. Initially most proponents suggested that human ancestors spent a period of time on the coastlines after the separation from the forefather of the chimpanzee (5-7 million years ago), and then left for land. But nowadays many of the leading waterside scientists suggest that the evolution to a marine environment continued.
Marc Verhaegen – one of the organizers of the conference – presented a controversial idea that Homo Erectus likely were shallow water divers. As a matter of fact their migration out of Africa was made exclusively along coastlines or rivers, and Homo Erectus had much larger brains and skulls than their predecessors (among many marine animals big skulls are equivalent to shallow diving). According to Verhaegen, Homo Erectus were much more adapted to a marine environment than for example Lucy and her species Australopithecus Afarensis. It is now clear that our big brains and sinuses as well as our voluntarily breath control evolved during Homo Erectus time on earth – which is highly likeable due to a rich intake of marine food and much time spent in water. Probably did also physiological traits as the human diving response, neonatal swimming reflexes and diving reflex evolve over time, not only during a short period of time 5-7 million years ago.
Hence, human evolution in an aquatic environment water was not only a historic incident that took place in Africa millions of years ago, but was an ongoing process throughout evolution of human beings. Our present aquatic adaptations are not remnants from an old way of living, as initially suggested by professor Alister Hardy and Elaine Morgan, but adaptations that were crucial also in the emergence of Homo Sapiens 200 000 years ago.
However, this theory is hard to accept within the anthropological community as they strongly emphasize a mosaic environment, suggesting that human beings were living in different environments throughout human history, just as we are living today. Human beings are thought to be able to live in any kind of environment and are not considered to be environmental specialists. But we can’t ignore that Homo Sapiens during most of her time as a living species has been living in an tropical environment feeding from an marine environment. As a matter of fact, we started to live on dry open spaces, like savannahs, much later.
Several newspapers wrote about the Human Evolution Conference, partly misunderstanding and misinterpreting the waterside theory. For example, Independent asked if “did humans come from the sea instead from the trees?”
Then – what can we learn from the new perspectives in the waterside theory? We have to start to accept that human beings have evolved in the same way as all other creatures – living predominantly in one habitat occupying only a small number of niches. We have not always been environmental generalists and we are still today – physiologically and biologically – much more adapted to a life along coastlines than a life on mountains or savannahs.
Conference on Human Evolution in London
In the conference, scientists will present new research and evidence highlighting the connection between humans and an aquatic lifestyle, as for example breath-hold diving, sea food/nutrition and water birth. Among the invited guests are Donald Johanson (the discoverer of Lucy) and David Attenborough (broadcaster and naturalist).
This conference clearly indicates that the Waterside-hypothesis (popularly the Aquatic Ape Theory) is getting more accepted in the scientific community. More and more scientists are now accepting that water has played an important role in human evolution, but the question is how big the aquatic impact has been.
Here you can find the program: Human Evolution Past, Present & Future – Anthropological, Medical & Nutritional Considerations.
Change in the programme for the second day: Day 2. Scars of Evolution
Visitors are welcome to admit posters on human evolution that will be presented during the conference. Prof. Erika Schagatay at Mid-Sweden University and I will present a poster on sea nomads of Southeast Asia focusing on their underwater vision, breath-hold diving and sea harvesting skills – characteristics that demonstrate that human beings still today can be highly adapted to the sea. I have also been invited to give a speech on Bajau Laut and their adaptations to the sea. See you in London!


































